Sigmoid diverticulitis / Laparoscopic colorectal resection (for cancer or diverticulitis)
60 year old lady with an episode of sigmoid diverticular perforation with was managed with antibiotics and other supportive measures. A surgery was avoided at this time. She settled well, however started experiencing recurrent incapacitating abdominal pain due to sigmoid diverticular disease. A laparoscopic sigmoid colectomy and colorectal anastomosis was electively performed. She was discharged on postoperative day 5. She is now completely pain and symptom free.
Colonic diverticulosis (grapelike outpouchings from the external surface of large intestine) is a very common problem in the western world. It is especially common in elderly ladies, patients with constipation, obesity and diet poor in roughage. With increasing life expectancy, changing lifestyle & changing food habits; diverticulosis is now seen commonly in Indian population too.

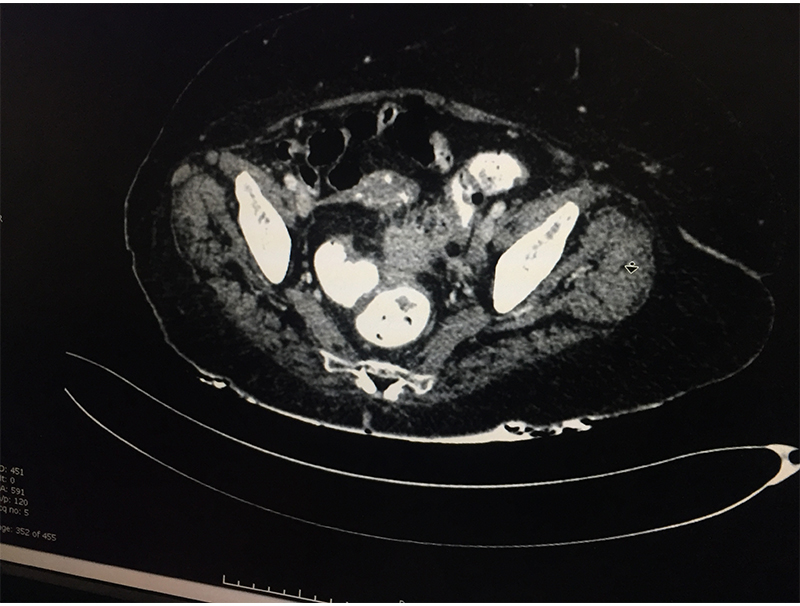
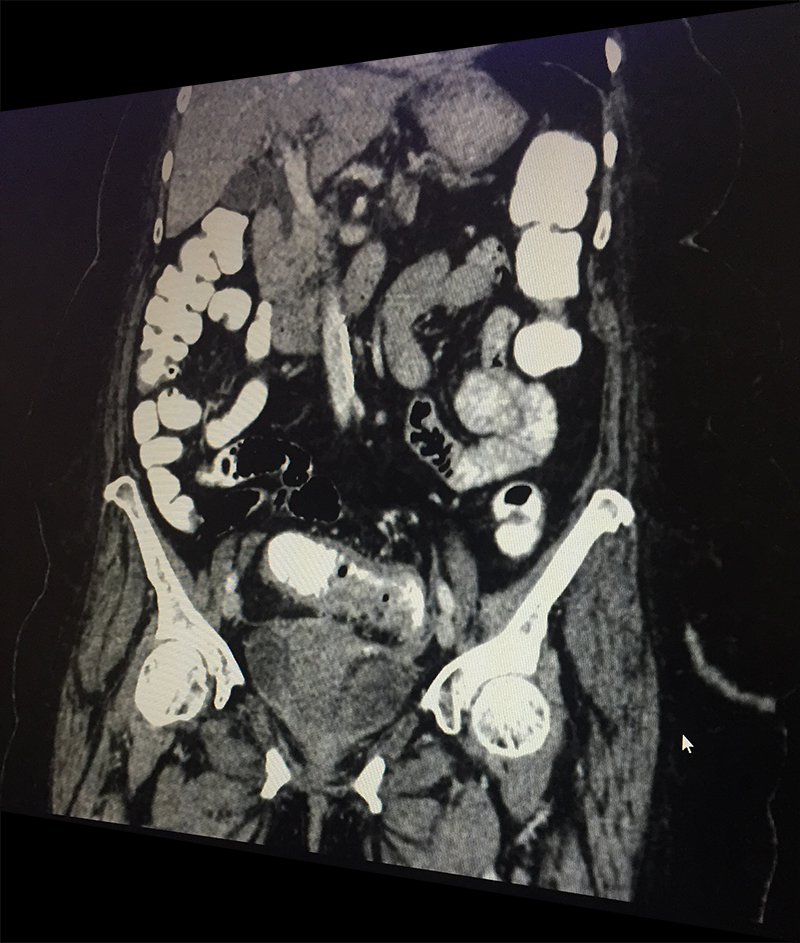
Diverticula can develop in any part of large intestine. However they are most common in the sigmoid colon (part of large intestine just before rectum begins lying in the left lower abdomen). It is this area in which diverticula most often pose problems for the patients.
Not all patients with colonic diverticula are symptomatic Some patients however may suffer from diverticular inflammation (diverticulitis) leading to an attack of acute abdominal pain. This may get complicated with a diverticular perforation followed by abscess formation in the abdomen or severe fecal contamination in the abdomen. All this can make a patient very sick endangering the life too due to sepsis. Patients with colonic diverticulosis can also present with fresh bleeding per rectum & narrowing of lumen / stricture formation leading to intestinal obstruction. Occasionally colonic malignancy may coexist with diverticular disease.
Not all patients with colonic diverticula are symptomatic. Diverticulosis is often picked up during a CT scan of abdomen for an unrelated problem or during a colonoscopy for vague abdominal discomfort or constipation. Most patients will have vague abdominal complaints or constipation of varying degree and can just do fine with high fibre diet & supplemental roughage in the form of esopgol. Few may need laxatives like lactulose, liquid paraffin, PEGLEC etcetra.
When a patient with acute abdominal pain is diagnosed (clinical suspicion) with a possible diverticulitis, he/she needs further investigations; blood & imaging study (CT scan of abdomen & pelvis) to confirm the diagnosis, rule out complications and plan the treatment based on the laid out guidelines. Most patients without complications & few with complications like contained perforation abscess are managed with antibiotics and occasionally with percutaneous drainage. Few patient require a laparoscopic lavage and drainage. Those with major perforation and fecal contamination require emergency surgery. It is done as an open procedure or by laparoscopic route depending on available expertise & patient condition. The involved sigmoid colon is resected and an end colostomy (bringing out the proximal end) is performed. The colon is reconstructed at a later date once patient has fully settled. If patient is too sick to tolerate a major surgery only a diverting colostomy (to bring the intestine lumen out on surface) is performed.
Patients who have responded well to conservative treatment for the initial attack, will be kept on low residue diet & laxatives for initial few weeks till the inflammation subsides completely. A colonoscopy is performed at the end of 6-8 weeks to rule out a malignancy which may coexist in 5% of patients and then patients are started on high fibre diet.
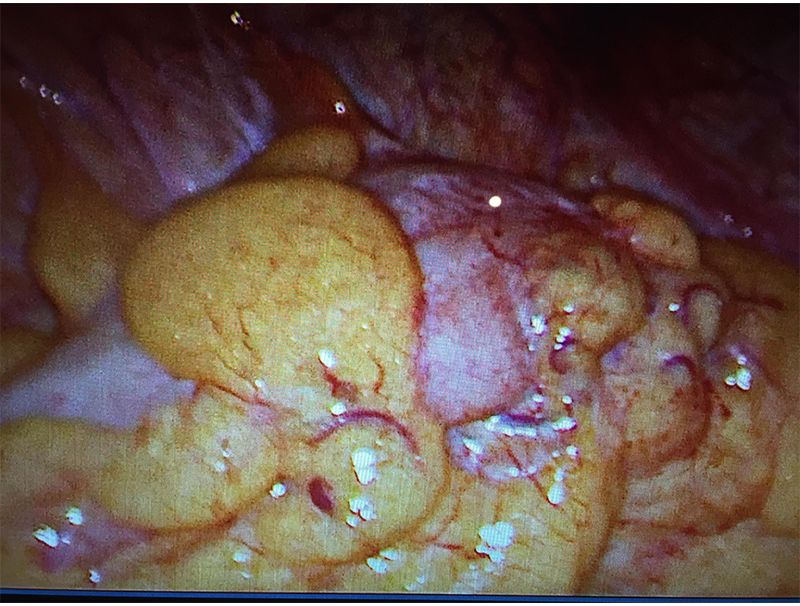
Patients who have been managed by conservative treatment in the initial attack may continue to suffer due to frequent minor attacks of acute inflammation or get recurrent abdominal pain due to chronic inflammation, adhesions, kinks, fibrosis or a stricture formation. This may require an elective surgery as was performed in above case. This surgery is safely performed laparoscopically reducing stay and discomfort and enhancing patient recovery.
Bleeding from colonic diverticulum is difficult to pinpoint, however when picked up is managed either by an angiographic embolization or an emergency surgery (colectomy)